|
home |
index |
units |
counting |
geometry |
algebra |
trigonometry |
calculus |
functions
analysis | sets & logic | number theory | recreational | misc | nomenclature & history | physics |
Final Answers
| ||||||||||
Related articles on this site:
- Water.
- Redox.
- Chemistry.
- The pH scale.
- Ancient acids.
- Acidity indicators.
- Organic Chemistry.
- Quantum Mechanics.
- Medical measurements.
- Photographic stop-bath.
- Molar (M) and normal (N) solutions.
- Chemical elements: The periodic table.
- Acetic acid and vinegar are rated by volume.
- Hydrate crystals are used to rate citric acid by weight.
- Electric dipole moment (EDM) of asymmetrical molecules.
- Avogadro's number: The number of things per mole of stuff.
- Physical Units: A tribute to the late physicist Richard P. Feynman.
- The detonation chemistry of TNT or amatol used to define a ton of energy.
- Chemical nomenclature: Basic sequential names (systematic or traditional).
Related Links (Outside this Site)NIST Chemistry WebBook | CAS Registry Numbers (CAS RN)Caveman Chemistry | Sciencemadness.org by Matthew Ernst. General Chemistry Starting Points (for students) by Steve Lower. |
Videos :
Edward Kent's Chemical Demonstrations | Alkali Metals in Water by Dnn87Light Bulb in HF. Martyn Poliakoff & Neil Barnes, filmed by Brady Haran.
The above concentrations at chemical equilibrium correspond to the following dimensionless equilibrium constants (cf. mass-action law) if we equate chemical affinities and concentrations (as an approximation).
The above equilibrium is properly described as 100% sulfuric acid. H2S2O7 can be viewed as sulfuric gas (SO3) dissolved in vitriol oil : H2SO4 + SO3 « H2S2O7 If more trioxide is dissolved than called for by the stoichiometry of pure sulfuric acid, then we effectively have sulfuric acid rated at more than 100%, because adding water to it would yield 100% sulfuric acid! Such stuff is called oleum or fuming sulfuric acid (the vapor is mostly sulfur trioxide). For better stability in storage, commercial concentrated sulfuric acid is usually rated at 98% (under 1 atm, there's an azeotrope at 98.3%, which boils at 338°C). By definition, 20% oleum is 20 kg of SO3 (80.0632 g/mol) dissolved in 80 kg of H2SO4 (98.0785 g/mol). Wikipedia : Sulfuric acid | Strong acids | Diprotic acids | Mineral acids A strong acid and a powerful oxidizing agent. Commercial concentrated nitric acid is 68% HNO3 which actually forms an azeotrope with water, boiling at 120.5 °C under 1 atm.
One of the earliest extant recipes for the preparation of
nitric acid is the distillation of
a mixture of niter (saltpeter; KNO3 )
green vitriol ( FeSO4 ) and alum.
This appears in De Inventione Veritatis
(part of the Pseudo-Geber
corpus, attributed to the Franciscan alchemist
Paul of Tarento,
who was active in the second half of the thirteenth century).
Wikipedia : Nitric acid | Oxidizing acid Stronger than nitric or sulfuric acid... Commercially available at a 72.5% concentrantion which forms an azeotrope with water at 1 atm, boiling at 203°C (indefinitely stable but hygroscopic). Perchloric acid was first obtained in 1816, by the Austrian Count Friedrich von Stadion, who observed the formation of potassium perchlorate by the action of sulfuric acid on potassium chlorate. An aqueous solution of perchloric acid results from the distillation of that mixture.
Wikipedia : Perchloric acid | Oxidizing acid Organic acids which owe their acidity to the -COOH group. Simplest examples are formic acid HCOOH and acetic acid CH3COOH.
Carboxylic Anhydrides :By dehydration, a carboxylic acid RCOOH gives a symmetrical anhydride (RCO)2O. Acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O is the simplest stable example at room temperature, since formic anhydride decomposes at 24°C. The simplest example of an asymmetrical carboxylic anhydride is acetic-formic anhydride. Wikipedia : Carboxylic acids | Organic acid anhydride The most acidic phenol (pKa = 0.38) is an explosive soluble in water.
Wikipedia : Picric acid 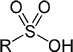 (2011-07-21) Tosylic acid and other sulfonic acids
(2011-07-21) Tosylic acid and other sulfonic acidsSulfonic acids owe their acidity to the -SO2(OH) group. Para-toluene-sulfonic acid or PTSA (CAS 104-15-4) is also called tosylic acid. It is a non-oxydizing strong acid (pKa = -2.8 in water) which is well-suited to the preparation of standard titration solutions because it's a soluble solid which can be conveniently weighed (172.202 g/mol). The negative pKa indicates a high dissociation constant in water: [ H3O+ ] [ CH3C6H4SO3- ] / [ CH3C6H4SO2(OH) ] = Ka = 630 Many other sulfonic acids are even much stronger than that: Halosulfuric Acids = Halosulfonic Acids :Being combinations of an halogen atom with a sulfonic group, these are best called halosulfonic acids. The alternate -sulfuric suffix merely evokes the structural similarity with the molecule of sulfuric acid. Fluorosulfuric acid FSO2(OH) is the strongest sulfonic superacid and one of the strongest acids commercially available. Chlorosulfuric acid ClSO2(OH) reacts violently with water to yield hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid: ClSO3H + H2O ® HCl + H2SO4 Bromosulfonic acid is a solid which decomposes at 8°C : 2 BrSO3H ® Br2 + H2SO4 + SO2 Iodosulfonic acid has apparently never been synthesized. Triflic Acid (TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH) :Triflic acid (trifluoromethanesulfonic acid) CF3SO2(OH) is a superacid first synthesized in 1954 by Robert N. Haszeldine (b. 1925) and J.M. Kidd. Wikipedia : Sulfonic acids | P-Toluenesulfonic acid A moderately strong acid used in acidimetry (non-hygroscopic crystals). This is a moderately strong acid: pKa = 1.05 In its solid form, sulfamic acid can be conserved indefinitely at room temperature. Because the crystals are not hygroscopic, they can be weighed accurately to prepare standard solutions used in acidimetry. For best accuracy, such solutions must be used promptly, as sulfamic acid degrades (slowly) when dissolved in water. The standard procedure is to calibrate a loosely prepared solution of a strong base (e.g. NaOH) by titration of a solution containing a precisely-measured mass of sulfamic acid crystals. (The volume of water used to dissolve the sulfamic acid is largely irrelevant but the crystals should be as pure as possible.) The basic solution so calibrated cam then be used for the titration of other acidic solutions. Sulfamic acid is considered a safe acidic cleaning agent for household use, mostly because (unlike stronger acids) it will not produce dangerous chlorine gas when accidentaly mixed with hypochlorite products. Wikipedia : Sulfamic acid A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor.
Wikipedia : Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory | Protonation | Deprotonation | Hydronium An acid is an electron-pair acceptor. A base is an electron-pair donor.
Arguing that only hydrogen compounds can be acids would be According to G.N. Lewis, an acid (A) and a base (B:) form an adduct AB, where the bond between A and B is a dative covalent bond (both electrons come from the base).
Lewis was nominated 35 times for the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Wikipedia : Lewis acids and bases | Octet rule | Gilbert N. Lewis (1875-1946) Going beyond the pH scale of dilute aqueous solutions.
Wikipedia : Acidity functions | Hammett acidity function | Louis Plack Hammett (1894-1987) Acids that are stronger than pure sulfuric acid.
Wikipedia :
Superacids
|
Carborane
Great affinities for protons. In aqueous solution, the hydroxide ion OH- has the highest basicity but there are compound that have greater proton affinity in dry environments.
Wikipedia : Superbases | Hydroxide ion | Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) Perchloric acid (HClO4) fluorosulfuric acid (HSO3F) and beyond. The strongest known superacid is fluoroantimonic acid H2F(SbF6).
Wikipedia :
Fluorosulfuric acid
|
Triflic acid
|
Leveling effect
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




